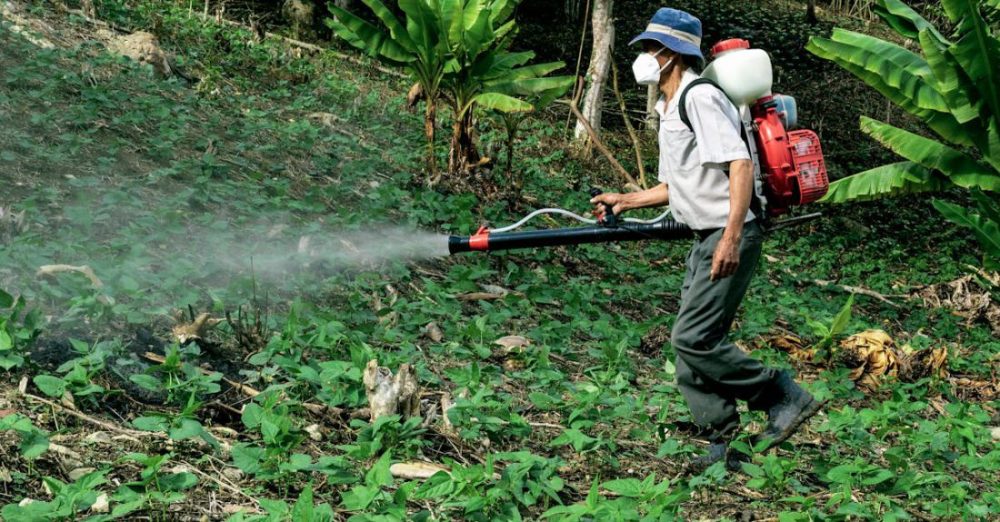
Using pesticides is a common practice in agriculture and pest control to protect crops and eliminate harmful insects. However, improper use of pesticides can have detrimental effects on the environment, human health, and non-target organisms. To ensure the safe and effective use of pesticides, it is essential to follow best practices. In this article, we will discuss the key guidelines for using pesticides responsibly.
Understanding Pesticides and Their Impact
Before using any pesticide, it is crucial to understand the type of pesticide you are dealing with and its potential impact on the environment and human health. Pesticides are chemicals designed to kill or control pests, including insects, weeds, and fungi. They can be toxic to humans, animals, and beneficial insects if not used correctly. It is important to read and follow the label instructions provided by the manufacturer to ensure safe and effective use.
Selecting the Right Pesticide
When choosing a pesticide, it is essential to select the right product for the target pest and the specific situation. Consider factors such as the type of pest, the area to be treated, and the potential risks associated with the pesticide. Some pesticides are broad-spectrum, meaning they can kill a wide range of pests, while others are more targeted and pose less risk to non-target organisms.
Applying Pesticides Safely
Proper application of pesticides is crucial to minimize risks to human health and the environment. Follow the instructions on the label carefully, including the recommended dosage, timing, and application method. Use protective equipment such as gloves, goggles, and masks when handling pesticides to prevent skin contact and inhalation. Avoid applying pesticides on windy days to prevent drift onto unintended areas.
Storing and Disposing of Pesticides
Proper storage and disposal of pesticides are essential to prevent contamination of water sources and soil. Store pesticides in their original containers in a cool, dry place away from food, pet food, and children’s reach. Do not mix pesticides unless recommended on the label, as this can create harmful chemical reactions. Dispose of empty pesticide containers according to local regulations and never reuse them for other purposes.
Monitoring and Record-Keeping
Regular monitoring of pest populations and the effectiveness of pesticide treatments is essential for making informed decisions about future applications. Keep detailed records of pesticide use, including the date, type of pesticide, application rate, and weather conditions. This information can help track trends in pest populations, identify potential issues, and improve overall pest management strategies.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach to pest control that emphasizes prevention, monitoring, and control methods to minimize the use of pesticides. By incorporating cultural, biological, and mechanical control methods, IPM aims to reduce reliance on chemical pesticides and promote sustainable pest management practices. When using pesticides as part of an IPM program, they should be considered a last resort after other control methods have been exhausted.
Training and Certification
Proper training and certification are essential for anyone involved in the handling and application of pesticides. Many countries require pesticide applicators to undergo training and obtain a license to ensure they have the knowledge and skills to use pesticides safely and effectively. Training programs cover topics such as pesticide toxicity, application techniques, safety precautions, and environmental protection measures.
Conclusion: Ensuring Safe and Effective Pesticide Use
By following these best practices for using pesticides, you can help protect the environment, human health, and beneficial organisms while effectively managing pest populations. Understanding the impact of pesticides, selecting the right product, applying pesticides safely, and incorporating IPM principles are key steps in responsible pesticide use. Remember to always read and follow label instructions, store and dispose of pesticides properly, monitor pest populations, and seek proper training and certification to promote sustainable pest management practices. By taking these precautions, you can minimize the risks associated with pesticide use and contribute to a healthier and more sustainable agricultural system.